Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Mizutani, Akihiko; ;
JNC TN9400 2000-013, 66 Pages, 2000/02
Feasibility study on a self-consistent fuel cycle system has been performed in the nuclear fuel recycle system with fast reactors. ln this system, the self-generated MAs (Minor Actinides) and LLFPs (Long-Lived Fission Products) are confined and incinerated in the fast reactor, which is called the "Equilibrium Core" concept. However, as the isotope separations for selected LLFPs have been assumed in this cycle system, it seems that this assumption is far from realistic one from the viewpoint of economy with respect to the fuel cycle system. ln this study, the possibility for realization of the "Equilibrium Core" concept is evaluated for three fuel types such as oxide, nitride and metallic fuels, provided that the isotopic separation of LLFPs is changed to the element one. This study provides, that is to say, how many LLFP elements can be confined in the "Equilibrium Core" with element separation. This report examines the nuclear properties of the "Equilibrium Core" for various combinations of LLFP incineration schemes from the viewpoints of the risk of geological disposal and the limit in confinable quantity of LLFPs. From the viewpoint of the risk of geological disposal estimated by the retardation factor, it is possible to confine with element separation for T , I and Se even in the oxide fueled core. From the standpoint of the limit of confinable amounts of LLFPs, on the other hand, T
, I and Se even in the oxide fueled core. From the standpoint of the limit of confinable amounts of LLFPs, on the other hand, T , I, S
, I, S , S
, S and Cs can be confined with element separation in case that the nitride fuel is chosen.
and Cs can be confined with element separation in case that the nitride fuel is chosen.
Oda, Chie; Ikeda, Takao*; Shibata, Masahiro
JNC TN8400 99-073, 112 Pages, 1999/11
In the safety assessment for geological disposal of high-level radioactive wastes (HLW), distribution coefficients (Kd) and diffusion coefficients of radionuclides are used to estimate the migration of radionuclides in a near-field of repository.  Sn is one of the important nuclides for the safety assessment in Japan and its behavior under reopsitory conditions has not been understood. This report provides the experimental informations for the sorption of Sn on bentonite, tuff and granodiorite, and the diffusion of Sn in a compacted bentonite. The Kd values of Sn on bentonite, tuff and granodiorite were determined by the batch-type sorption experiments as l0
Sn is one of the important nuclides for the safety assessment in Japan and its behavior under reopsitory conditions has not been understood. This report provides the experimental informations for the sorption of Sn on bentonite, tuff and granodiorite, and the diffusion of Sn in a compacted bentonite. The Kd values of Sn on bentonite, tuff and granodiorite were determined by the batch-type sorption experiments as l0
 10
10 [ml/g], 10
[ml/g], 10
 10
10 [ml/g] and 10
[ml/g] and 10
 10
10 [ml/g], respectively. The sequential extraction experiments for adsorbed Sn on bentonite were also performed to investigate its desorption behavior. These experimental results indicated that the mechanisms of sorprion onto bentonite were dominated by the sorption reactions on smectite and pyrite and consisted of reversible and irreversible sorption on solid and stable fixation in solid. On the other hands, the apparent diffusion coefficients (Da) in compacted bentonite were measured by the diffusion experiments as 10
[ml/g], respectively. The sequential extraction experiments for adsorbed Sn on bentonite were also performed to investigate its desorption behavior. These experimental results indicated that the mechanisms of sorprion onto bentonite were dominated by the sorption reactions on smectite and pyrite and consisted of reversible and irreversible sorption on solid and stable fixation in solid. On the other hands, the apparent diffusion coefficients (Da) in compacted bentonite were measured by the diffusion experiments as 10 [m
[m /sec] and l0
/sec] and l0 [m
[m /sec] for dry densities of 0.4[g/cm
/sec] for dry densities of 0.4[g/cm ] and 1.0[g/cm
] and 1.0[g/cm ], respectively. Moreover, the Kd values in compacted bentonite were calculated according to the relationship with the measured Da values, and the solubilities in the porewaters of compacted bentonite were calculated by use of the calculated Kd and the obtained diffusion plofiles. It is found that the derived solubilities almost agreed with the solubiliies of amorphis SnO
], respectively. Moreover, the Kd values in compacted bentonite were calculated according to the relationship with the measured Da values, and the solubilities in the porewaters of compacted bentonite were calculated by use of the calculated Kd and the obtained diffusion plofiles. It is found that the derived solubilities almost agreed with the solubiliies of amorphis SnO reported by Amaya et al. (1997), however, the derived Kd values were lower than that measured from the batch-type sorption experiments.
reported by Amaya et al. (1997), however, the derived Kd values were lower than that measured from the batch-type sorption experiments.
Lothenbach, B.*; Ochs, M.*; Wanner, H.*; Yui, Mikazu
JNC TN8400 99-011, 340 Pages, 1999/01
This report provides thermodynamic data for predicting concentrations of palladium Pd, lead Pb, tin Sn, antimony Sb, niobium Nb and bismuth Bi in geologic environments, and contributes to an integration of the JNC chemical thermodynamic database, JNC-TDB (previously PNC-TDB), for the performance analysis of geological isolation system of high-level radioactive wastes. Besides treating hydrolysis in detail, this report focuses on the formation of complexes or compounds with chloride, fluoride, carbonate, nitrate, sulfate and phosphate. Other important inorganic ligands (sulfide for lead and antimony, ammonia for palladium) are also included. In this study, the specific ion interaction theory (SIT) approach is used to extrapolate thermodynamic constants to zero ionic strength at 25 C.
C.
Oda, Chie; *
JNC TN8400 98-001, 14 Pages, 1998/11
Solubilities of amorphous stannic oxide, SnO (am) in Na-ClO
(am) in Na-ClO -Cl-SO
-Cl-SO aqueous systems were measured to quantitatively investigate the influences of the ligands OH
aqueous systems were measured to quantitatively investigate the influences of the ligands OH , Cl
, Cl and SO
and SO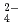 on solubilities. They were also measured in bentonite equilibrated solutions to discuss the behavior of tin under a repository condition of a high-revel radioactive waste. The solubility data in sodium perchlorate media in the range of pH from 6 to 11 showed pH dependency, and the hydrolysis constants of tin (IV) were determined (Amaya, et al., 1997). No significant changes in solubilities with the variation in Cl
on solubilities. They were also measured in bentonite equilibrated solutions to discuss the behavior of tin under a repository condition of a high-revel radioactive waste. The solubility data in sodium perchlorate media in the range of pH from 6 to 11 showed pH dependency, and the hydrolysis constants of tin (IV) were determined (Amaya, et al., 1997). No significant changes in solubilities with the variation in Cl , SO
, SO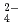 concentrations were observed in Na-ClO
concentrations were observed in Na-ClO -Cl-SO
-Cl-SO aqueous systems, so this indicates that chloride and sulfate species were less effective than hydroxide complexes. On the other hand, solubilities in bentonite equilibrated solutions were higher than solubilities of other experiments in simple systems. These results suggest that (1) other complexes of tin except hydroxide, chloride or sulfate complexes of tin (IV) may dominantly exist in aqueous phase, (2)solid phase other than SnO
aqueous systems, so this indicates that chloride and sulfate species were less effective than hydroxide complexes. On the other hand, solubilities in bentonite equilibrated solutions were higher than solubilities of other experiments in simple systems. These results suggest that (1) other complexes of tin except hydroxide, chloride or sulfate complexes of tin (IV) may dominantly exist in aqueous phase, (2)solid phase other than SnO (am) may limit the solubility of tin under repository conditions.
(am) may limit the solubility of tin under repository conditions.
Ikeda, Takao*; Amaya, Takayuki*; Chiba, Tamotsu*
PNC TJ1281 97-004, 42 Pages, 1997/03
It is very important to explain the sorption mechanisms of relevant radionuclides, for the performance assessment of geological disposal and for the technical development of engineering barrier system. In the previous studies 1993-1996, these tests were carried out to understand sorption mechanism of SN; -solubility tests -sorption tests onto bentonite, pure montmorillonite, A-FEO(OH) -extraction tests from these minerals -sorption tests onto tuff as a next step, these tests were carried out ragarding SN in this study; -diffusion tests (in-diffusion) -tests for effect of SN concentration and ionic strength on sorption -sorption tests onto granite -tests for effect of coexistent ions on solubility
Myochin, Munetaka; Iwase, Masanori*
PNC TY8604 96-001, 32 Pages, 1996/03
no abstracts in English
PNC TJ1281 95-008, 55 Pages, 1995/03
1. Introduction 2. Items of study 3. Prediction of Sn aqueous species and acquision of thermodynamic data 3.1 Test condition 3.2 Test method 3.3 Result 3.4 Discuion 3.5 Analysis 3.6 Conclusion 4. Acquisition of Sn distribution coefficients on bentonite, pure montmorillonite and  -FeO(OH) 4.1 Sorption test 4.4.1 Test condion 4.1.2 Method 4.1.3 Result 4.1.4 Discussion 4.1.5 Conclusion 4.2 Sequential eraction test 4.2.1 Test condition 4.2.2 Method 4.2.3 Result 4.2.4 Discussion 4.5 Conclusion 5. Mechanisms of Sn sorption onto bentonite 6. Apparent diffusion coecient in compacted bentonite 6.1 Preliminary analysis to predict diffusion of Sn inentonite 6.2 Test condition 6.3 Method 7. Conclusio
-FeO(OH) 4.1 Sorption test 4.4.1 Test condion 4.1.2 Method 4.1.3 Result 4.1.4 Discussion 4.1.5 Conclusion 4.2 Sequential eraction test 4.2.1 Test condition 4.2.2 Method 4.2.3 Result 4.2.4 Discussion 4.5 Conclusion 5. Mechanisms of Sn sorption onto bentonite 6. Apparent diffusion coecient in compacted bentonite 6.1 Preliminary analysis to predict diffusion of Sn inentonite 6.2 Test condition 6.3 Method 7. Conclusio